Bandwidth
Bandwidth is a very important characteristic of a network, which can be used for measuring the network performance. Bandwidth can have two different values:
- BW in hertz and
- BW in bits per second
BW in Hz:
It is the range of frequencies present in a composite signal. It can also be defined as a range of frequencies that a channel can pass through without much attenuation.
BW in bits per second:
We can also define bandwidth as the number of bits per second (BPS) that a channel can transmit. For eg., the BW of Fast Ethernet is 100 Mbps i.e. that network can transmit 100 Mbps.
Relationship :
- There is a clear relationship between the bandwidth in Hz and BW in bps. With increase in BW in Hz, there is an increase in bps bandwidth.
- The relation between them depends on whether baseband transmission is being used or transmission with modulation is being used.
Signal and Channel Bandwidths :
- We can two different bandwidths:
- Signal bandwidth 2. Channel bandwidth
- Signal bandwidth Bs is defined as the range of frequencies contained in the signal.
- Whereas the bandwidth of the channel Bc is the range of frequencies that is passed by a channel.
- If the bandwidth of the input signal is larger than the channel bandwidth, then the output of the channel with not contain all the frequencies of the input signal.
- Fig. shows a typical digital signal at the input and the output is of different shape than input, if the channel BW is less than signal BW.
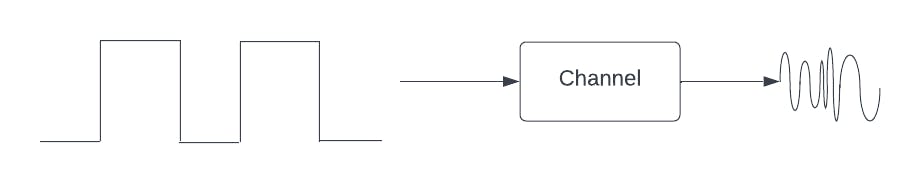
- If the signaling rate of input signal is increased, then the channel bandwidth has to be increased so as to pass the signal without any change in shape of the signal.
- The bandwidth is also important in deciding the channel capacity C of the transmission system.
- The channel capacity C of a transmission system is the maximum rate at which bits can be transferred reliably.
- The channel capacity should be as high as possible and to increase C.
- We have to increase the channel bandwidth Bc.
Bandwidth analogy with Plumbing
Data is to available bandwidth as water is to the size of the pipe.
In other words, as the bandwidth increments so does the sum of information that can stream through in a given sum of time, similar to as the breadth of the pipe increments, so does the sum of water that can stream through amid a period of time.
Say you're streaming a film, somebody else is playing an internet multiplayer video game, and a few others on your same organize are downloading records or utilizing their phones to observe online recordings. It's likely that everybody will feel that things are a bit drowsy on the off chance that not constantly beginning and ceasing. This has got to do with the bandwidth.
To return to the plumbing similarity, accepting the water pipe to a house (the transmission capacity) remains the same measure, as the home's spigots and showers are turned on (information downloads to the gadgets), the water weight at each point (the seen "speed" at each gadget) will reduce—again, since there's as it were so much water (transfer speed) accessible to the domestic (your network).
Put another way: the bandwidth is a fixed amount based on what you pay for. While one person may be able to stream a high-def video without any lag whatsoever, the moment you begin adding other download requests to the network, each one will get just their portion of the full capacity.
Illustration of bandwidth being split between three devices
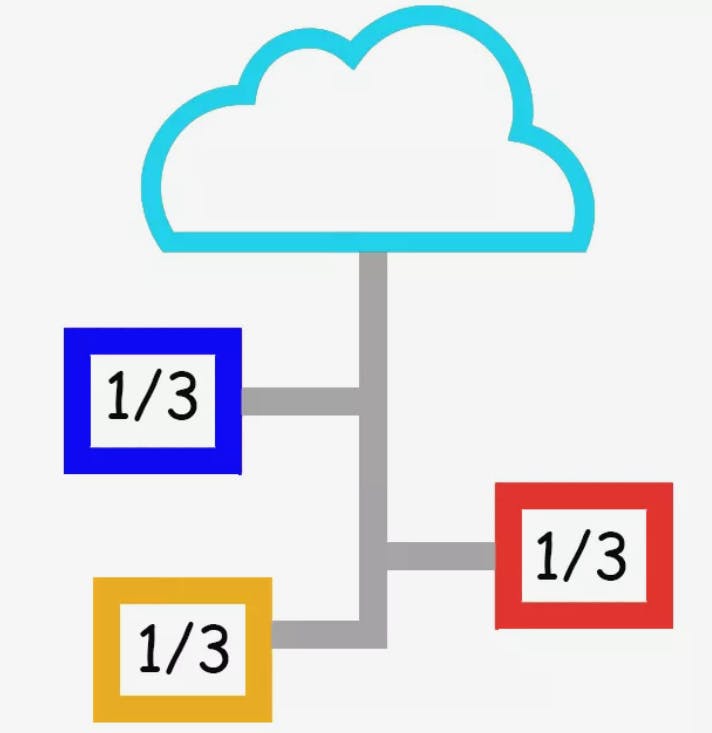
For eg., in case a speed test recognizes my download speed as 7.85 Mbps, it implies that given no interferences or other bandwidth-hogging applications, I seem download a 7.85 megabit (or 0.98 megabytes) record in one moment. A small math would tell you that at this permitted transfer speed, I might download around 60 MB of data in one miniature, or 3,528 MB in an hour, which is identical to a 3.5 GB file...pretty near to a full-length, DVD-quality movie.
So, whereas I seem theoretically download a 3.5 GB video record in an hour, in the event that somebody else on my organize tries to download a comparable record at the same time, it would presently take two hours to total the download since, once more, the organize as it were grants x sum of information to be downloaded at any given time, so it presently must permit the other download to utilize a few of that transfer speed, too.
Actually, the arrange would presently see 3.5 GB + 3.5 GB, for 7 GB of add up to information that should be downloaded. The transmission capacity capacity doesn't alter since that's a level you pay your ISP for, so the same concept applies: a 7.85 Mbps organize is attending to presently take two hours to download the 7 GB record rather like it would take fair one hour to download half that sum.